Navigating the Learning Landscape with ADHD: Unveiling the Challenges and Strategies
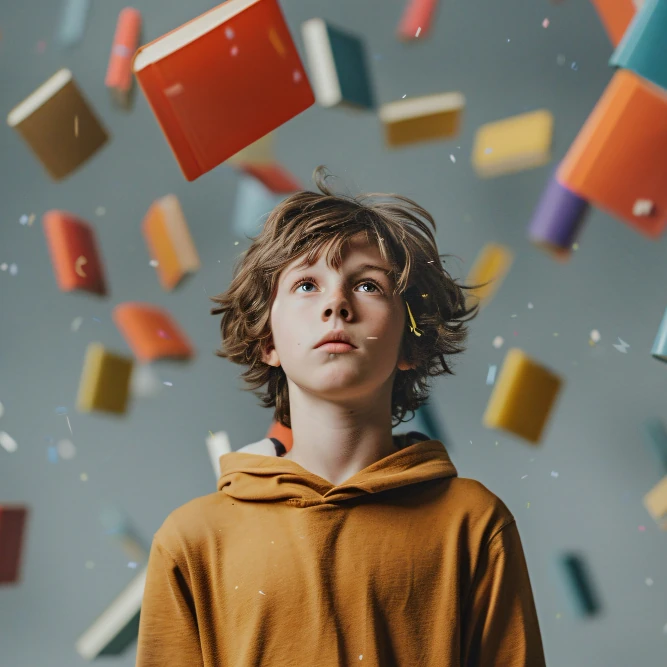

The journey of learning is unique for each individual, shaped by various factors that contribute to one’s cognitive and emotional development. However, for those navigating the terrain with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), the path can be peppered with distinct challenges that require a nuanced understanding. In this blog post, we’ll explore how ADHD affects learning and shed light on strategies that can pave the way for a more supportive educational experience. Attention Challenges ADHD is often characterized by difficulties in sustaining attention. In a traditional learning environment, where focus is key, individuals with ADHD may find it challenging to stay engaged in tasks for extended periods. Distractions, both internal and external, can divert attention away from the intended learning objectives. Strategy: Implementing structured routines, breaking down tasks into manageable chunks, and incorporating interactive learning methods can help maintain focus. Additionally, providing a quiet and minimally distracting learning environment can create a conducive space for concentration. Impulsivity Impulsivity is another hallmark of ADHD, making it difficult for individuals to think before acting. In a classroom setting, impulsive behavior can disrupt the flow of lessons and hinder effective learning for both the individual and their peers. Strategy: Teaching and encouraging self-monitoring techniques can empower individuals with ADHD to pause and reflect before responding impulsively. Introducing mindfulness practices can also contribute to increased self-awareness and better impulse control. Working Memory Challenges Individuals with ADHD may experience difficulties with working memory, affecting their ability to retain and manipulate information over short periods. This can pose challenges in tasks that require sequential processing and quick recall. Strategy: Employing visual aids, such as charts, diagrams, and graphic organizers, can enhance memory retention. Additionally, incorporating repetition and review into the learning process can reinforce key concepts and improve information retention. Hyperactivity The hyperactive component of ADHD can manifest as excessive fidgeting, restlessness, and difficulty sitting still. In a classroom setting, this behavior can be misconstrued as disruptive, leading to potential social and academic challenges. Strategy: Providing opportunities for movement breaks and incorporating hands-on learning activities can channel excess energy in a positive direction. Flexible seating arrangements that accommodate different learning styles can also create a more inclusive and comfortable environment. Conclusion Understanding how ADHD affects learning is the first step towards creating an inclusive and supportive educational experience. By embracing tailored strategies that cater to the unique needs of individuals with ADHD, educators and caregivers can empower them to navigate the learning landscape more effectively. Through a collaborative effort, we can ensure that every learner, regardless of their cognitive profile, has the opportunity to thrive and unlock their full potential.
Unlocking Learning Potential: The Impact of Executive Function on Education

Introduction Executive function, a set of mental processes that facilitate goal-directed behavior, is a crucial factor in a child’s ability to learn and thrive in an educational setting. In this blog, we’ll explore the various facets of executive function and how they influence the learning experience. What is Executive Function? Executive function encompasses a range of cognitive skills, including attention control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and self-control. These skills act as the brain’s “CEO,” managing and coordinating other mental processes to achieve specific goals. Attention Control: The Gateway to Learning Attention is the foundation of all learning. Children with strong executive function can sustain attention, filter out distractions, and focus on the task at hand. This skill is crucial for absorbing information in the classroom and during independent study. Working Memory: The Mental Notepad Working memory allows students to temporarily hold and manipulate information. A robust working memory enables effective problem-solving, comprehension, and the ability to follow multi-step instructions—essential skills for academic success. Cognitive Flexibility: Adapting to Change Learning environments are dynamic, and cognitive flexibility allows students to adapt to new information and shifting demands. Children with well-developed executive function can easily transition between tasks, subjects, and classroom activities. Self-Control: The Key to Academic Persistence Self-control is vital for regulating emotions and impulses. Students with strong executive function can manage frustration, delay gratification, and stay focused on long-term goals, contributing to academic persistence and achievement. Executive Function Challenges in Learning Disabilities Some students may face challenges in developing executive function, often associated with learning disabilities such as ADHD or dyslexia. Understanding and addressing these challenges early on can significantly improve educational outcomes. Strategies to Support Executive Function in Learning: Collaboration Between Home and School Effective communication between parents and teachers is essential. Sharing insights about a child’s executive function strengths and challenges ensures a cohesive and supportive approach to their education. Conclusion Recognizing the impact of executive function on learning is a crucial step in creating a positive and effective educational experience for every child. By understanding and nurturing these cognitive skills, parents and educators can empower students to overcome challenges and unlock their full learning potential.
The Art of Tidiness: A Guide to Keeping Your Life in Order

Introduction In the hustle and bustle of our daily lives, it’s easy for chaos to creep in and take over. Whether it’s your living space, workspace, or digital realm, maintaining organization is key to reducing stress and increasing productivity. Let’s delve into the art of tidiness and explore some practical tips to keep your things organized. Declutter Regularly The first step in achieving organization nirvana is decluttering. Take a critical look at your belongings and ask yourself, “Do I really need this?” If the answer is no, it might be time to part ways. Regular decluttering sessions prevent unnecessary accumulation and make it easier to maintain a tidy space. Everything Has a Home Assign a designated spot for each item you own. This applies to everything from your keys to your favorite pen. When everything has a specific home, it’s easier to put things back where they belong, reducing the chances of a messy space. Categorize and Prioritize Group similar items together and prioritize their importance. This principle works wonders in various aspects of life—whether it’s your wardrobe, kitchen, or work tasks. By categorizing and prioritizing, you can easily locate what you need and tackle important tasks first. Invest in Storage Solutions Storage solutions are your best friends when it comes to organization. Utilize bins, baskets, shelves, and drawer dividers to maximize space and keep things orderly. Clear containers are particularly handy, allowing you to see the contents without rummaging through. Digital Organization In the digital age, it’s crucial to extend your organizational skills to the virtual realm. Create folders on your computer, organize your email inbox, and delete unnecessary files. Digital clutter can be just as overwhelming as physical clutter, so stay on top of it. Develop Consistent Habits Building habits is key to maintaining organization. Make it a habit to tidy up for a few minutes each day, whether it’s before bed or as soon as you wake up. Consistency is the secret sauce to an effortlessly organized life. The Power of Lists Lists are powerful tools for organization. Create to-do lists for daily tasks, shopping, or long-term goals. Crossing items off a list not only provides a sense of accomplishment but also keeps you focused and organized. One In, One Out Rule To prevent the influx of unnecessary items, implement the “one in, one out” rule. For every new item you bring into your space, consider letting go of something old. This simple practice helps maintain a balance and prevents clutter from piling up. Conclusion Keeping your things organized is not just about appearances; it’s a lifestyle that promotes efficiency, reduces stress, and enhances overall well-being. Embrace the art of tidiness, and watch as a sense of order transforms your life, one organized space at a time.
Mastering Time: A Guide to Effective Time Management

Introduction Time is a finite resource, and managing it efficiently is crucial for personal and professional success. In a world that constantly demands our attention, honing effective time management skills can be a game-changer. Let’s explore practical strategies to help you make the most of your time and boost productivity. Set Clear Goals Begin by defining your short-term and long-term goals. Break them down into smaller, actionable tasks. This clarity will serve as a roadmap, guiding you through your day with purpose. Prioritize Tasks Not all tasks are created equal. Identify the most critical and time-sensitive activities. The Eisenhower Matrix, which categorizes tasks into urgent/important, not urgent/important, urgent/not important, and not urgent/not important, can be a helpful tool for prioritization. Create a Schedule Establish a daily or weekly schedule to allocate time for specific tasks. Be realistic about how much time each activity requires, and include breaks to prevent burnout. Stick to your schedule as much as possible, but be flexible enough to adapt to unexpected challenges. Learn to Say No Recognize your limits and don’t be afraid to decline tasks or projects that may compromise your ability to meet existing commitments. Saying no is a powerful skill in maintaining focus and preventing overcommitment. Utilize Time Blocking Allocate specific blocks of time for similar tasks. For instance, group meetings together to prevent interruptions throughout the day. This helps maintain concentration and minimizes context-switching. Embrace Technology Explore productivity tools and apps to streamline your workflow. Calendar apps, task management tools, and project management platforms can help you stay organized and on track. Set reminders and deadlines to keep yourself accountable. Break Down Big Tasks Large projects can be overwhelming. Break them into smaller, more manageable tasks. This not only makes the workload more digestible but also provides a sense of accomplishment as you complete each subtask. Minimize Multitasking Contrary to popular belief, multitasking can reduce overall productivity. Focus on one task at a time to enhance concentration and the quality of your work. Reflect and Adjust Regularly assess your time management strategies. What’s working well? What could be improved? Adjust your approach based on your reflections to continually refine your time management skills. Practice Self-Care Balancing work and personal life is essential for sustained productivity. Ensure you allocate time for rest, relaxation, and activities you enjoy. A well-rested mind is more focused and efficient. Conclusion Effective time management is a skill that can be cultivated with dedication and practice. By setting clear goals, prioritizing tasks, and implementing practical strategies, you can take control of your time and achieve a more balanced and fulfilling life. Remember, it’s not about managing time; it’s about managing yourself within the time you have.
Mastering the Art of Prioritization: A Student’s Guide to Success.

Introduction As a student, juggling assignments, exams, and extracurricular activities can feel like a daunting task. The key to navigating this academic maze successfully lies in mastering the art of prioritization. In this blog, we’ll explore effective strategies for students to prioritize tasks and manage their time efficiently. Create a To-Do List Start by listing all your tasks for the day or week. This could include assignments, study sessions, and any other commitments. Breaking down your workload into manageable chunks makes it easier to prioritize and tackle each task systematically. Identify Urgency and Importance Use a prioritization matrix to categorize tasks based on urgency and importance. Focus on tasks that are both urgent and important first, followed by those that are important but not urgent. Be mindful of time-sensitive deadlines and allocate your efforts accordingly. Set Clear Goals Establish specific, measurable, and achievable goals for each task. This clarity helps you stay focused and motivated. Instead of vague goals like “study for biology,” specify a goal like “complete biology notes for chapters 1-3 by 4 PM.” Consider Your Energy Levels Take note of your energy levels throughout the day. Prioritize tasks that require higher concentration and focus during your peak energy hours. This ensures that you tackle demanding tasks when you’re at your mental best. Learn to Say No While extracurricular activities are essential for personal development, it’s crucial to strike a balance. Learn to say no to additional commitments when your plate is already full. Overloading yourself can lead to burnout and compromise the quality of your work. Break Down Larger Tasks Large projects or assignments can be overwhelming. Break them down into smaller, more manageable tasks. This not only makes the workload seem less daunting but also allows you to make steady progress over time. Use Time Blocking Allocate specific blocks of time for different types of tasks. For example, designate a block for studying, a block for assignments, and a block for relaxation. This structured approach helps prevent procrastination and ensures that all aspects of your academic and personal life are addressed. Be Flexible Recognize that unexpected events or changes in priorities may occur. Stay adaptable and be willing to adjust your plans accordingly. A flexible mindset allows you to navigate challenges without feeling overwhelmed. Reflect and Evaluate Regularly assess your priorities and tasks. Reflect on what worked well and what could be improved. Adjust your strategies based on your experiences to continually refine your approach to prioritization. Conclusion Mastering the art of prioritization is a skill that will serve you well throughout your academic journey and beyond. By creating a structured plan, identifying key priorities, and staying adaptable, you can effectively manage your time and workload. Remember, it’s not about doing everything; it’s about doing the right things at the right time. Prioritize wisely, and you’ll find yourself achieving success in both your academic and personal pursuits.
Navigating Life with Precision: Understanding Executive Function

Introduction Executive function is the unsung hero of our cognitive processes, quietly orchestrating the symphony of tasks that make up our daily lives. It’s like the conductor of an orchestra, ensuring that each instrument plays its part in harmony. In this blog, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of executive function, exploring its role, challenges, and strategies for enhancing it. What is Executive Function? Executive function refers to a set of mental skills that help individuals manage, plan, organize, and execute tasks. Think of it as the brain’s command center, responsible for decision-making, problem-solving, and regulating emotions. These skills are crucial for success in various aspects of life, from academic and professional pursuits to personal relationships. The Three Pillars of Executive Function Challenges Associated with Executive Dysfunction Many conditions and situations can impact executive function, leading to challenges in daily life. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), traumatic brain injuries, and certain neurodevelopmental disorders are often linked to executive dysfunction. Stress, lack of sleep, and aging can also affect these cognitive processes. Strategies for Enhancing Executive Function Conclusion Executive function is the backbone of effective cognitive processing, influencing our ability to navigate life’s challenges. By understanding its components and implementing strategies to support it, individuals can unlock their full potential and lead more organized, focused, and fulfilling lives. So, let’s give a well-deserved spotlight to the unsung hero that is executive function.
How We Help Children With Executive Function

As a parent, you want your child to be successful in all aspects of their life, and that includes their academic performance. However, some children may struggle with certain skills that are necessary for success, such as executive function skills. This is where Midwest Educational Therapy & Associates (META) comes in. META is a team of highly trained professionals who specialize in helping children with executive function skills. Executive function skills are a set of cognitive processes that are responsible for goal-directed behavior. These skills include planning, organizing, initiating, and monitoring actions, as well as working memory, cognitive flexibility, and self-regulation. Children with executive function difficulties may have trouble with completing tasks, managing time, staying focused, and regulating their emotions. META’s team of experts uses a research-based approach to assess and identify a child’s executive function difficulties. They then develop an individualized plan to help the child improve their skills. The plan includes a variety of evidence-based strategies and techniques that are tailored to the child’s specific needs. One of the strategies used by META is cognitive training. This involves specific exercises and activities that help the child develop their cognitive skills. These exercises are designed to target areas of weakness and build up strengths. The exercises can be done in person or remotely, depending on the child’s needs. Another strategy used by META is coaching. This involves working with the child to help them develop specific skills, such as time management and organization. The coach provides guidance and support, helping the child to set goals and track progress. The coach also helps the child to develop strategies for staying focused and managing distractions. Need Help With Your Child? META also works closely with parents and teachers to ensure that the child’s needs are being met. They provide regular progress reports and collaborate with other professionals involved in the child’s care, such as therapists and psychologists. In addition to helping children with executive function skills, META also provides support for children with learning difficulties, such as dyslexia and ADHD. They offer a range of services, including assessments, therapy, and academic support. If you’re concerned about your child’s executive function skills or other learning difficulties, don’t hesitate to reach out to META. They can help your child develop the skills they need to succeed academically and in life. With their evidence-based approach and individualized plans, you can be confident that your child is receiving the best possible support.
What Is Executive Function In Children?
What Is Executive Function In Children? Executive function (EF) is a critical set of skills that help children manage their thoughts, emotions and behavior. EF skills allow children to plan and execute tasks, stay on task, keep track of information, and inhibit impulsive behaviors. EF skills are important for success in school and in life. Poor EF skills can lead to problems such as difficulty completing homework assignments, trouble following instructions, and impulsively blurting out answers in class. EF skills can be improved through targeted interventions and practice. Parents can help their children develop EF skills by providing structure, clear expectations, and regular feedback. What are some specific executive function skills? Some specific executive function skills include: -Task initiation: The ability to begin and complete tasks. -Time management: The ability to plan and track time spent on tasks. -Goal setting: The ability to identify and achieve goals. -Organization: The ability to keep track of materials and tasks. -Flexibility: The ability to adapt to changing situations. -Self-control: The ability to inhibit impulsive behaviors. What can parents do to help their children develop executive function skills? There are many things that parents can do to help their children develop executive function skills. Some tips include: -Providing structure and clear expectations: Children with poor EF skills need structure and clear expectations in order to stay on task. Parents can help by creating routines for homework and chores, and providing regular feedback on tasks. -Helping children set goals: Children with poor EF skills often have difficulty staying motivated. Helping children set and achieve small goals can help them stay focused and motivated. -Encouraging organization: Children with poor EF skills often lose track of materials and tasks. Parents can help by providing organizational tools such as folders, checklists, and calendars. -Encouraging flexibility: Children with poor EF skills often find it difficult to adapt to changing situations. Parents can help by modeling flexibility and providing opportunities for children to experience a variety of situations. -Teaching self-control: Children with poor EF skills often have difficulty inhibiting impulsive behaviors. Parents can help by teaching children how to pause before responding and how to manage strong emotions. If you need help with executive function in your child or have questions, please fill out the form or give us a call.